This post is all about sleep hacking. Strategies to improve health energy and mind while getting better rest in less time.
Understanding Sleep And Your Body

Basics of sleep
Sleep is known as the state of unconsciousness in which a person can be aroused. So there are two types of things-:
- Sleep: It is when if I tap you on the shoulder I shake you really hard. You’re unconscious but you can wake up.
- Coma: A coma is where no matter how hard to shake someone or poke someone or whatever they do they can’t get a Waken.
Sleep is essential for our body to be able to normally function. And it also affects our mental and physical health. So the less sleep you get it all kind of all to your physical and mental health. Accordingly, If you’ve ever pulled an all-nighter or not slept or got very few amounts of hours of sleep over a long period of time. Your body takes steps taken a toll on and it has to compensate for it. So you quickly realize that you quickly figure it out.
Sleep also allows our bodies to fight diseases and induce sickness. So the less sleep you get over a period of time. The more prone you are to possibly get sick. Catching something whatever the case is because your body doesn’t have the necessary strength with its autoimmune system to be able to battle these diseases.
Importance of sleep
Sleep deprivation results in a decrease in your body temperature and also your immune system functions. The decrease in your immune system function can result in you getting sick or catching something that you might not have been able to catch. If you had the proper amount of sleep.
Metabolic activity of your brain decreases after you stay awake for 24 hours or more. So what that basically means is your reflexes and activities in the brainwaves of your membrane are much slower or much more decreased if you don’t get sleep within a 24 hour period. Because your brain is tired and it hasn’t had the ability to shut off and rest.
Emotional social functions are maintained optimally during sleep. So this just basically means that you’re still functioning while you’re sleeping. It’s not like your whole body just turns off. But it’s functioning in an optimal manner where you’re able to get the rest while still getting the motors running within you.
Substances that alter sleep
Caffeinated drinks or anything like coffee, soda or things like that or even pills. Can stimulate alter parts of your brain that might make it a lot harder for you to be able to sleep.
Cigarettes are other nicotine-induced products can also alter your sleep. So whether it’s smoking a cigarette, smoking hookah, smoking marijuana. Whatever the case is depending on when you smoke it can alter your sleep by then making it harder or easier sometimes to sleep.
Alcohol and I’m sure a lot of you if you’ve ever tried alcohol. It’s very easy to fall asleep when you drink alcohol. But your sleep cycles aren’t the same.
Sometimes some prescribed drugs have side effects. So that’s another thing that you want to keep in mind. When you take any of these substances to see how it can potentially alter your sleeping state.
Myths about sleep
MYTH 1: That your body just quickly to various sleep schedules. Actually, it takes about a week at the minimum to adjust. If you go on a trip or you’re jet-lagged or whatever the case is. When you switch your body clock to different timing. It doesn’t just do it after a day or night. It actually takes up to a week at the minimum. Usually about 10-15 days.
MYTH 2: Extra sleep at night can cure you of problems with the teeth during the day. So it’s not about the quantity of sleep but the quality of sleep. So if anyone’s ever slept 12 or 13 hours whatever the case is. They probably know that it’s not that easy to just feel good because you slept a lot. You can still feel fatigued. It’s all about the quality of your sleep.
MYTH 3: You can make up for lost sleep by sleeping more on the weekends. Yes, this does help with something known as sleep debt which is basically if you slept very little on a certain day but you end up sleeping a bit more on the weekends. You can kind of catch up and get the rest of your brain and body function needs. But this isn’t the healthiest way to do it and it’s highly not recommended.
How Much Sleep Do You Really Need

Don’t sleep less, sleep smarter
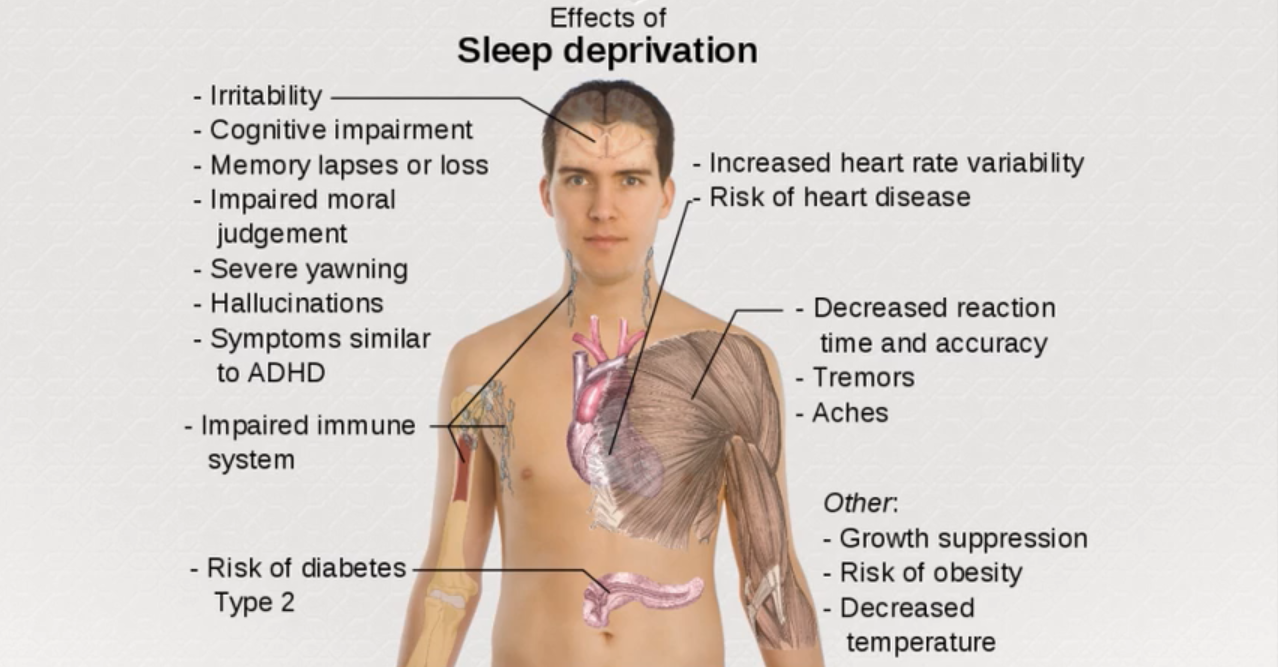
So this chart kind of shows you a couple of effects of sleep deprivation. So we definitely don’t want to do that. And as you can see. Sleep deprivation over time can cause a better ability in your brain cognitive impairment. You might start losing memory lapse. You might start yawning severely you might even get hallucinations. And some people also suffer symptoms very similar to ADHD. So these are all things that can possibly happen to you mentally.
And now looking at other parts of your body. It increases your heart rate and also the risk of heart disease for you. Impair your immune system. It increases your risk of type 2 diabetes. It decreases your reaction time and accuracy. You might get aches and tremors that you wouldn’t get normally. And then lastly other things that are also increased when you don’t sleep or you are deprived of sleep over time is growth suppression. So if you’re so growing, it can definitely suppress your growth. It can definitely increase your risk of obesity and it also decreases your body temperature. So these are all things to keep in mind.
The goal is to get you guys be sleeping about six hours while feeling good which won’t cause these effects of sleep deprivation or any other adverse effects to your body.
Sleep Cycles & Stages

The stages of sleep
Transition to sleep:
In this, you fall asleep. They did only about five minutes long and your eyes are actually slowly moving under your eyelids as your mass muscle activity ends up slowing down. So this is the period where your body’s really kind of calming down and going into the resting mode. And it only lasts about five minutes typically.
Light sleep:
This is the very first stage of sleep that’s lasting for about 10 to 25 minutes. As your eye movements do stop your heart rate does slow down and your body temperature begins to decrease. So with the light sleep stage, it’s very easy to wake someone up or some kind of noise or flashing light or little things like that can really quickly jolt them awake. So they’re not in a deep sleep period or anything like that.
Deep sleep:
So after you’ve gone to the light sleep machine you go into stage three which is known as Deep sleep. You are difficult to awaken and when you are woken up you feel disorientated and groggy for a few minutes. So your brain waves are extremely slow in this stage and this is kind of the part where you’re actually a bit harder to wake up.
REM sleep:
So this usually takes place after 17 to 90 minutes of sleep. You enter the sleep or dreaming is taking place lucid dreams all that stuff take place during this stage. Your eyes start moving rapidly your breathing is a bit shallow and your heart rate and blood pressure will also increase. And this is the place where you basically get the best rest to be refreshed for the next day.
The architecture of sleep
Throughout the night your sleep follows a rather predictable pattern that goes back and forth from deep sleep to the more alert stages of sleep. So once you enter REM. You’re not staying in REM for the entire night. You kind of keep going back and forth through these patterns.
So the amount of time that you spend in the stages of sleep changes as the night progresses. So the most deep sleep occurs in the beginning half of your night and your REM sleep stages will get longer on a little bit better as you get later into the night.
Quality sleep and internal clocks
Your biological clock is regulated over a 24 hour period of time. So basically when you sleep the way sleep works it’s going through a period of 24 hours and that’s what your mind. Also calculates sleep. So at night, your body responds to the darkness by producing something known as melatonin which makes you sleepy.
So when it’s kind of darker outside and the lights are dimmer and that kind of thing your brain kind of starts to realize that it’s getting closer to the time where it needs to shut down. During the day though the sunlight triggers your brain to inhibit even more melatonin so that you’re awake and alert. So if you have a lot of lights on in the house bright lights, TVs, and stuff like that it’s automatically going to make your brain think “OK I’ve got to be awake and alert because at that time.”
Things such as travel, staying up late, artificial light, and even irregular sleeping patterns can really disrupt your internal clock. So any time these types of things do take place you wanna be patient you really want to make sure that you’re doing the proper things necessary to make sure that you’re getting quality sleep. Because especially with travel stuff like that jetlag you tend to lose sight of what’s important and how to sleep and all that good stuff you really want to keep all those things in mind.
Sleep debt
Let’s say, a lot of people tend to do this is they’ll sleep maybe four or five hours throughout the week throughout Monday through Friday and then they’ll think on Saturday and Sunday they can sleep 10 hours and make up for all the lost sleep that they had during the week.
So this is something that actually to an extent does work and something that you can do but it’s a very unhealthy and poor way of making up sleep and you really don’t want to get to a point where you’re in debt with your sleep. You have to make up your sleep and all that stuff.
Tips for getting and staying out of sleep debt
So it’s okay to settle short term sleep debt by getting an extra hour or two per week. But nothing more than that. For example, Monday and Tuesday you get really busy, you’re only able to get like four hours of sleep or something like that. At that point, you might be able to make up an extra couple hours throughout the rest of the week. But you don’t want to make it a habit.
Keep a sleeping diary to record when you go to bed and when you wake up so you can really see how effective you are and how long you’re sleeping for. One trick or technique that a lot of people like to do is they like to wake up right at the end of REM. So they feel really fresh. Basically remixers every 90 minutes. Let’s say you go to bed at 12:00. So your first REM period will end at 1:30. And then the next one at 3:00. Then the next one at 4:30 and then the next one at 6:00. So let’s say you want to wake up at 6:00, you’d specifically fall asleep by midnight. At 6:00 a.m. when you wake up you can get the end of your REM stage. So you’re going be the fresh and aware and alert when you do wake up.
Make your sleep priority as you schedule a time for work and other types of commitments. So people oftentimes are too busy scheduling everything else. But they totally forget to make sleep a priority year top commitment to them in their lives. And I just highly recommend that you plan things around sleep as well because sleep is extremely crucial to the well-being of your mind and to the health and wellness of your body.