This might surprise you to learn that a lot of the things that you think were invented recently were actually invented as far back as thousands of years ago. Here are the 10 oldest versions of modern technology.
1. Automatic doors – 50 B.C.
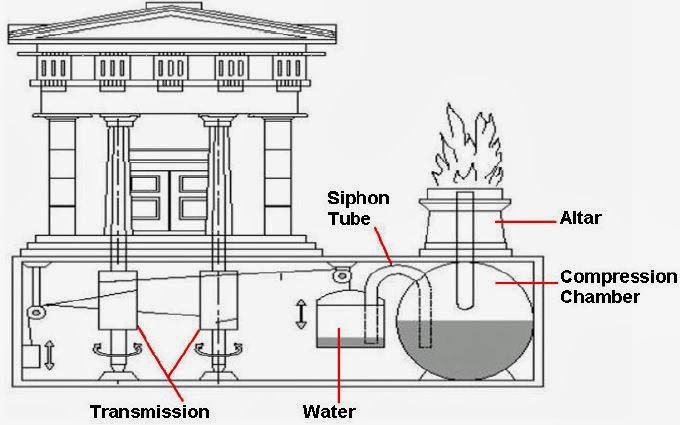
Modern, automatic sliding doors were invented in 1954 by Lou Hewitt and Dee Horton, but they weren’t actually the first doors to open for a person on their own.
Nearly 2,000 years ago, a genius mathematician and mechanical inventor named Heron of Alexandria, invented a way to have a door open itself automatically. His idea involved steam and water pressure, which were new concepts at the time. A fire would be lit by a temple’s priest, and its heat would build up pressure inside a brass container. That pressure would, in turn, displace water already there. The water would get pumped into some holding containers, which would lower under the new weight of the liquid and slowly pull open the door.
2. Navigation – 1920’s/1932
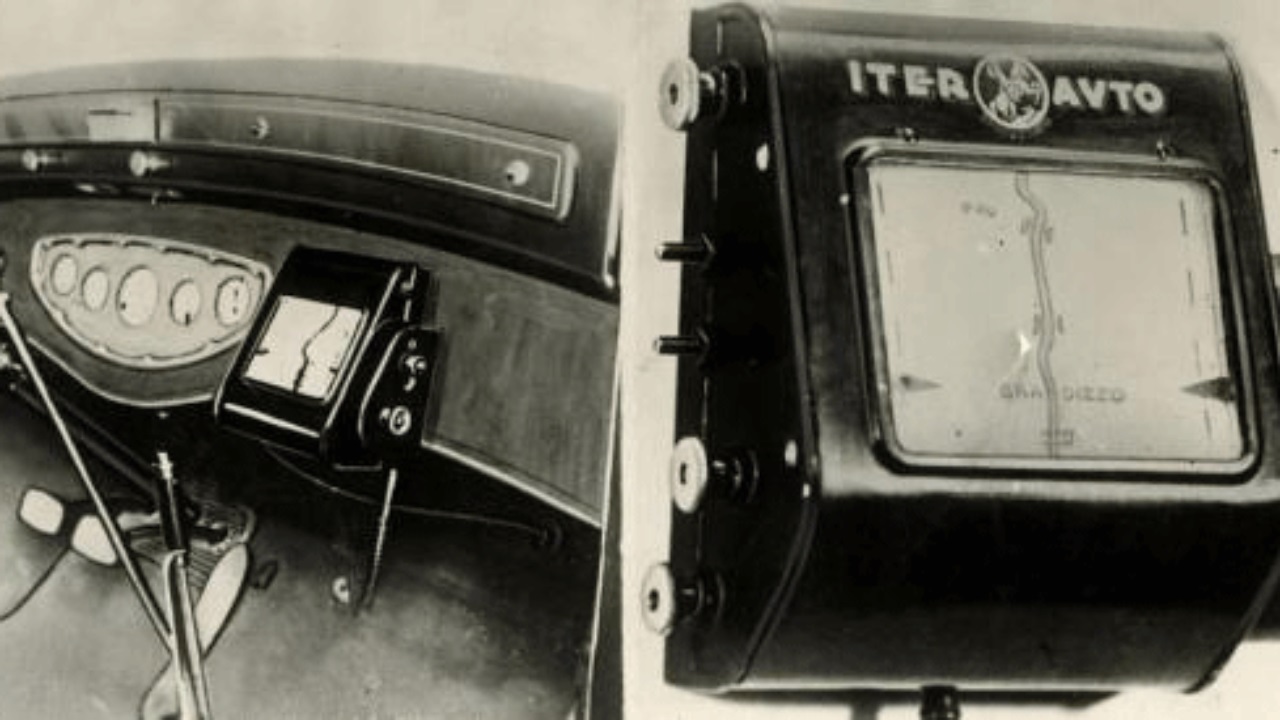

These days, it seems most people would be unable to get from place to place without the assistance of a GPS.
The global positioning system which has personally saved me many times that tells us where we are through the satellites at any given time.
Before the invention of GPS, however, people relied on maps and have done so for thousands of years. But in the early 1920s, devices would appear that would bridge the gap. Wearable on the wrist, the Plus Fours Routefinder consisted of two reels as well as an interchangeable map cartridge which kind of resembled a scroll. Users would wind the map as they traveled along and followed the streets as it was laid out on it. 10 years later, versions of this contraption came out meant for the car. Using the vehicle’s speed, the scroll would move accordingly.
3. E-Reader – 1922
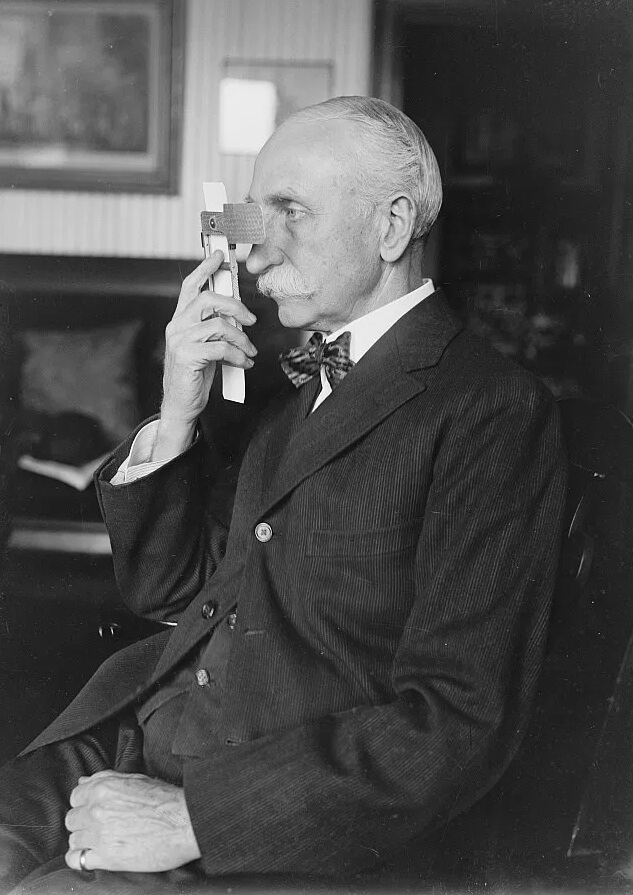

Before Kindles began saving trees, the only way to read a book was to purchase.
Amazon launched the Kindle in 2007, before which, in 1998, it’s predecessor, the Rocket eBook, was unsuccessfully sold by NuvoMedia. But neither of those were technically first.
That distinction goes to a product from the early 1920s, Fiske’s Reading Machine. Invented by Rear Admiral Bradley Allen Fiske, the reading machine was a metal, handheld instrument with a magnifying glass for one eye and a small flip-out shield to block the sight of the other. Books were written in tiny fonts on a long, thin strip that slid through the device and under the magnifying eyepiece.
One of the first books available for it was Mark Twain’s Innocent Abroad, which was around 93,000 words, but fit onto 13 cards.
4. Chewing gum – 7000 B.C.

When you think of chewing gum, you likely think of a minty or sweet-flavored candy full of preservatives to keep its consistency, but it actually has a history that goes back thousands of years.
Before Juicy Fruit, Bazooka Joe, and Trident, there was a tree resin, sweetgrass, and wax, not nearly as appetizing as a stick of spearmint, but was still enjoyed by the ancient Mayans and several other colonies.
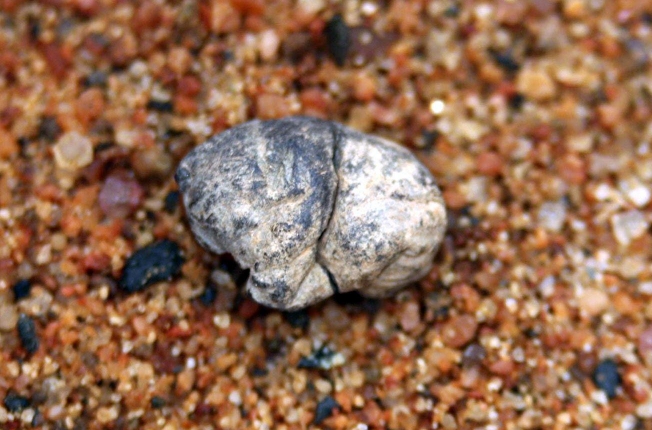
Centuries ago, ancient Greeks began chewing mastiche, which is made from the secretions of the mastic tree, but the oldest pieces of gum ever discovered were found on what is today the island of Orust in Sweden.
Three wads of fossilized gum were found in total, each of them made of birch resin. Experts claim the chewed-up pieces are around 9,000 years old, meaning that they date back to around 7,000 B.C.
5. Vending machines – 215 B.C. – 100 A.D

We live in a world of convenience, able to buy almost anything that we require from a machine.
Everything from food and beverages to hygiene products, toys, and even marijuana can be purchased from vending machines.
There are actually places where you can get everything on your grocery list exclusively by using them.
All of that said, we’re far from being the first human beings to live in a world that has automated machines that trade products for coins.
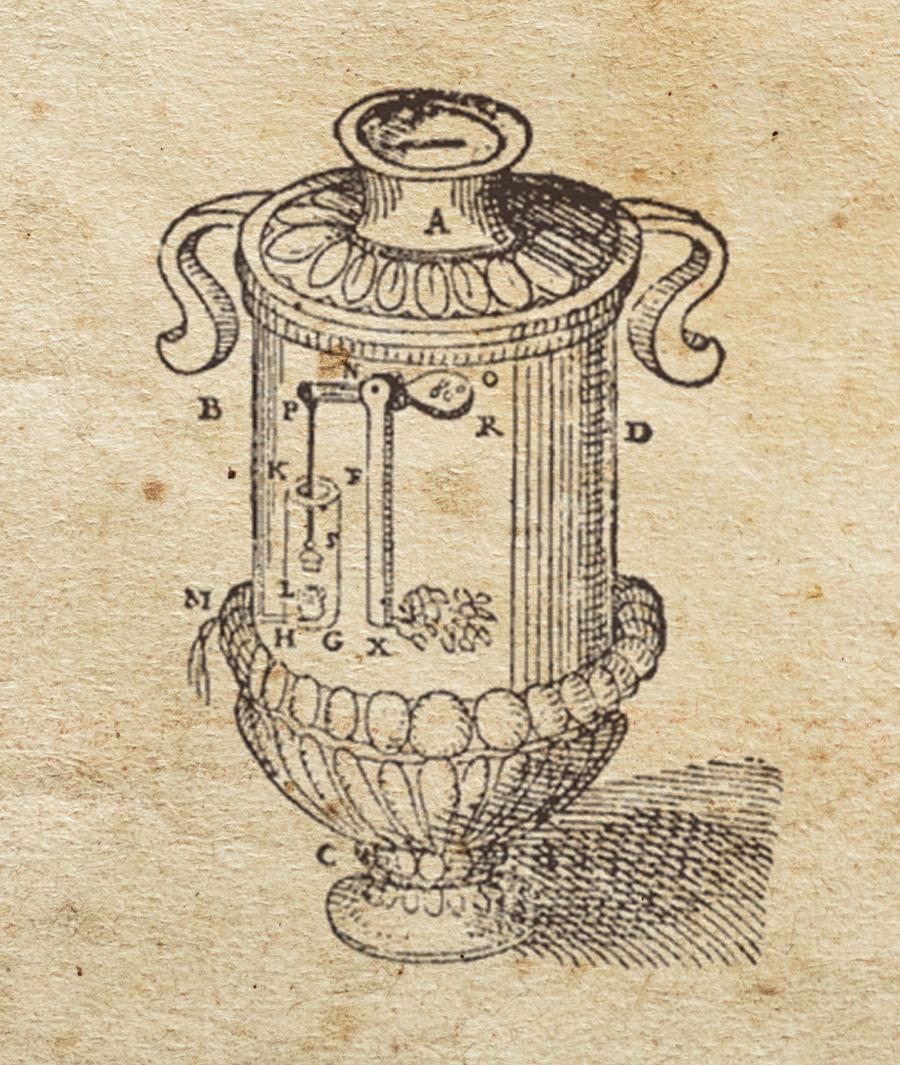
The first documented vending machine was established in ancient Egypt. It was built sometime between 215 B.C. and 100 A.D. and housed inside a temple inside the city of Alexandria. The “automated” device featured a system in which a worshiper would feed it a five drachma Greek coin and receive a small amount of holy water.
6. Toy car – 5500 B.C.

In a discovery that has quite a few archeologists scratching their heads, a collection of ancient items was uncovered in Mardin, Turkey that included a tablet that served as a deed for the sale of a garden, dolls, working whistles, and, incredibly, what appears to be a tiny car.
Made of stone, the car, which researchers believe was a toy or model of some kind, has two axles and four wheels. Complete with a space that looks like a windshield, it more closely resembles a modern-day tractor than an automobile. But obviously, neither of those could have been used as inspiration to complete the artifact, since it predates both of them by thousands of years.
The car was over 7,500 years old, dating back to the Stone Age. And many experts claim it’s the earliest evidence of the wheel being invented.
7. Calculator watch – 17th century

While calculator watches would obviously be considered a 20th century invention, and the Apple Watches and Fitbits 21st century ones, none of them can be called the first tiny calculators that can be worn on the hand.
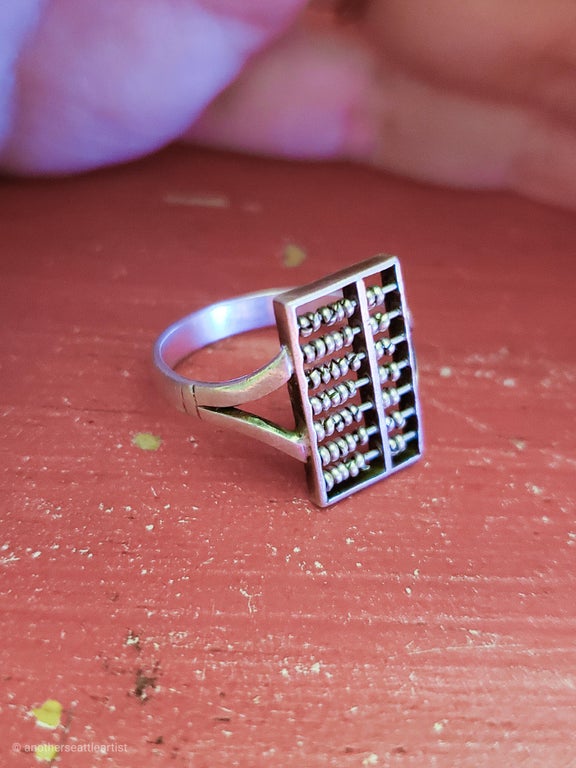
For that device, we have to go back hundreds of years to the Shang Dynasty of the 17th century. Believe it or not, the first wearable calculator was a super small abacus that was attached to a ring.
Now nicknamed the smart ring, the device was invented by an unidentified man in China who was clearly ahead of his time. The abacus was only 1.2 centimeters in width, so small it was nearly impossible to operate by hand, instead of requiring small, pointy items such as pins to move each bead along one of seven rods.
8. Hair extensions – 1300 B.C.
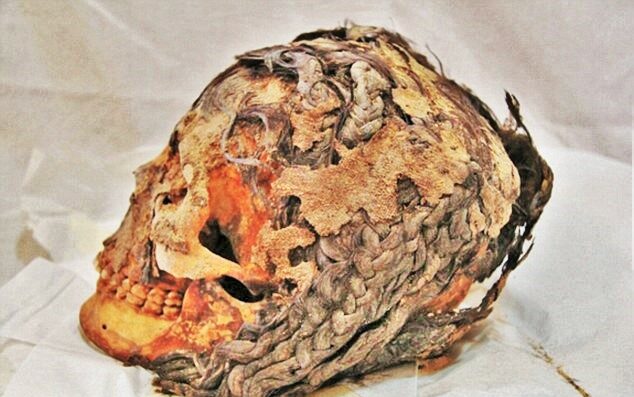
In 2014, some human remains uncovered in Egypt were being analyzed by researchers when a surprising discovery was made.
Many of the skulls still had hair preserved on them. However, some of them had more than that. They had hair extensions.
One skull belonged to a woman who lived over 3,300 years ago and had been buried shortly after the city she was found in, Amarna, was built. She had a total of 70 extensions, which were likely donated by multiple donors.
A number of other remains with extensions of various colors were also found. Whether they had their hair lengthened for everyday life or were simply given it for their funerals was unclear. But was is clear is that ancient Egyptians had the ability to add hair extensions and practiced doing so.
9. Google Earth/Street View – 1908-1979

Several decades before you were able to look at your home’s roof using Google Earth or at your front door with Google Street View, there were actually methods of doing just that, only much more difficult to obtain.
In 1908, Dr. Julius Neubronner, a German apothecary, patented pigeon photography, in which the birds would have small cameras strapped to their chests and would periodically take pictures while the animals were flying overhead.
The resulting aerial photos may have contained a few blurry feathers, but they managed to show the area from above.
In 1979, when a team of students and faculty from MIT attached a camera to a car and created the Aspen Movie Map, the first version of Street View, though only of Aspen, Colorado.



